
Written by Ar. Parul Agarwal
Under the Guidance of Ar. Dhruv Bhaskar; Chief Architect, Dustudio, Auroville
Living in an earth full of resources, one of the most abundantly found is mud.
Mud is not only used as a rural or traditional material but has grown about as one of the most ecological approach to modern design. Man must realize the importance of mud, and make the most of its abundance on this planet. As people in the cities consider mud as a traditional material with many limitations, this in turn affects the thinking of the rural class. Mud is a material so easy to mold and adapt to various situations or regions. Auroville is one of those few places in the India that has made optimum use of the mud that is locally available and has invented various new techniques in the field of architecture using mud. Mud requires knowledge to build but it is a material that is ignored too, due to less knowledge about the material. The main objective of this research is to promote mud architecture among the rural class who now believe that mud is a low class building material. In order to learn the various techniques and to throw light on the new techniques that is possible with mud. The objective is to change the false perception of mud as a poor building material or a building material just for the poor. Based on various regions and people, the dissertation is compiled towards creating a positive approach on dirt expression among the people.
Mud has been the most essential of building materials since the dawn of the man. Most of the buildings in India are made of mud brick and it is a growing construction boom in India. Mud is a building material which has already being tested and tried for thousands of years. As the times are changing and as people are getting more familiar with modern or contemporary architecture, the techniques of using mud in construction are decreasing every day, as mud is usually considered as a vernacular material. Unfortunately these days so many of us think that we can only build “properly” and “satisfactorily” by using such items as reinforced concrete, cement blocks, burnt bricks, etc. On the contrary the manufacture of steel and cement for reinforced concrete is now called “energy intensive”. So, we ought to develop our consciences about not using expensive and imported materials. The natural and reasonable retort to this entire sort of thing is “But what CAN we use? What does not need a lot of energy for its manufacture? One answer is to – use more stone but in many parts of our country there is no usable stone. The other answer is that in many areas there is mud and, believe it or not but the National Census will show you that numerically, there are more houses in India made of mud than of any other material. As the mud is usually available as a local material, the mud of each region all over the country can itself be used for its very own characteristic. It is used in modern day construction and the method of using it is very different based on the location, the people, the technique, the cost, all greatly varies. Mud may be old fashioned, but it could be successfully used even for the best houses, and, indeed, if all of us are to go into 21st century with a roof over our 700-800 million beads, we will only be able to do it if we put mud into its rightful status. Mud has its limitations, but so do all materials. Studying these limitations and then build within those limitations, is the challenge.
Mud, creating the Dirt Expression: in the present scenario.
Mud is one those ancient practices that evolves every day. One must understand that as it is such an ancient practice its familiarity with the people is just commendable. Being an age old practice it is used in almost every town or city is some way or the other. As it evolves with time, the essence of mud is not lost but just improved.
Through various case studies, it will be easier to understand that mud is evolved so much that it being used in various permutation and combinations, in different parts of the world in different ways. It behaves as one material that binds all cultures together. As we are in the 21st century, the ideology of mud architecture is slowly drifting away towards the perception of a more rural practice. The value of mud architecture needs to be revived and spread across to the people, as it is one of those few techniques that are beneficiary to the people in multiple ways.
While studying the soil that is available in various parts of India, a clear light would be reflected on how they adapt to the people living in the region and how the people affect the techniques of mud architecture. With the growing need for shelters for a large scale of people it is necessary to educate them about mud architecture as; mud is a material that is found in large quantities all over the world. Also to change the idea that due to urbanization the traditional practices to be aborted or replaced with a few that according to the society is considered more superior than what could be more convenient and functional.
The main objective of this study is to:
Limitations of Mud:
Red Soil – One such soil that will be used in the Proposal
Most of the red soils have come into existence due to weathering of ancient crystalline and metamorphic rocks. The main parent rocks are acid granites and gneisses, quartzite and felspathic. The color of these soils is generally red, often grading into brown, chocolate, yellow, grey or even black. The red color is due more to the wide diffusion rather than to high percentage of iron content. These soils are spread on almost the whole of Tamil Nadu, parts of Karnataka, south-east of Maharashtra, eastern parts of Andhra Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Orissa and Chota Nagpur in Jharkhand. The texture of these soils varies from sand to clay, the majority being loams. On the uplands, the red soils are thin, poor and gravelly, sandy or stony and porous, but in the lower areas they are rich, deep dark and fertile.
Proposal of a Community Toilet:
There is a small village called Periyarmudaliar Chavadi, which is at junction of the east coast road on the way to Puducherry.
Living in the current location at that time, I observed the growing need for a community toilet and sanitation. The people of the village were using a common tap in order take a shower in the open. If there was the possibility to provide them with a community toilet, there would be nothing better for the village and the people around the village. As such there are no public toilets anywhere close the village or around it. There would be no better option for the building material than Mud as Auroville is rich in mud and this village marks the entrance to Auroville. Hence the proposal of a public toilet made of mud where the fittings to the foundation is all made of mud coupled with elements like cement, steel and stone.
This site is apt as it lies at the center of the village, hence can be accessed by all and also it is just lying as a free space where the villagers are struggling with a water pipe. The proposal is purely based on the surrounding conditions and for the better of the village and its sanitation.
The site is 24 meters by 18 meters wide, where it’s divided into two halves, which belong to two different people, where one is for sale and the other just left empty.
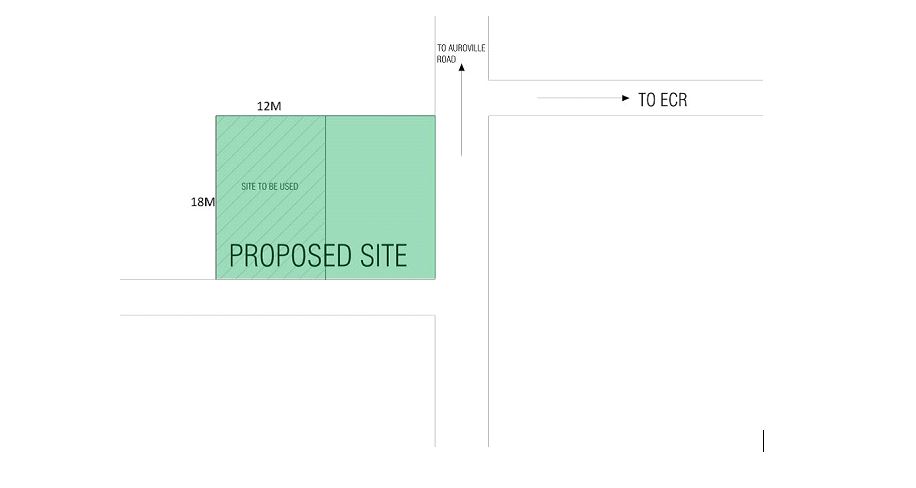
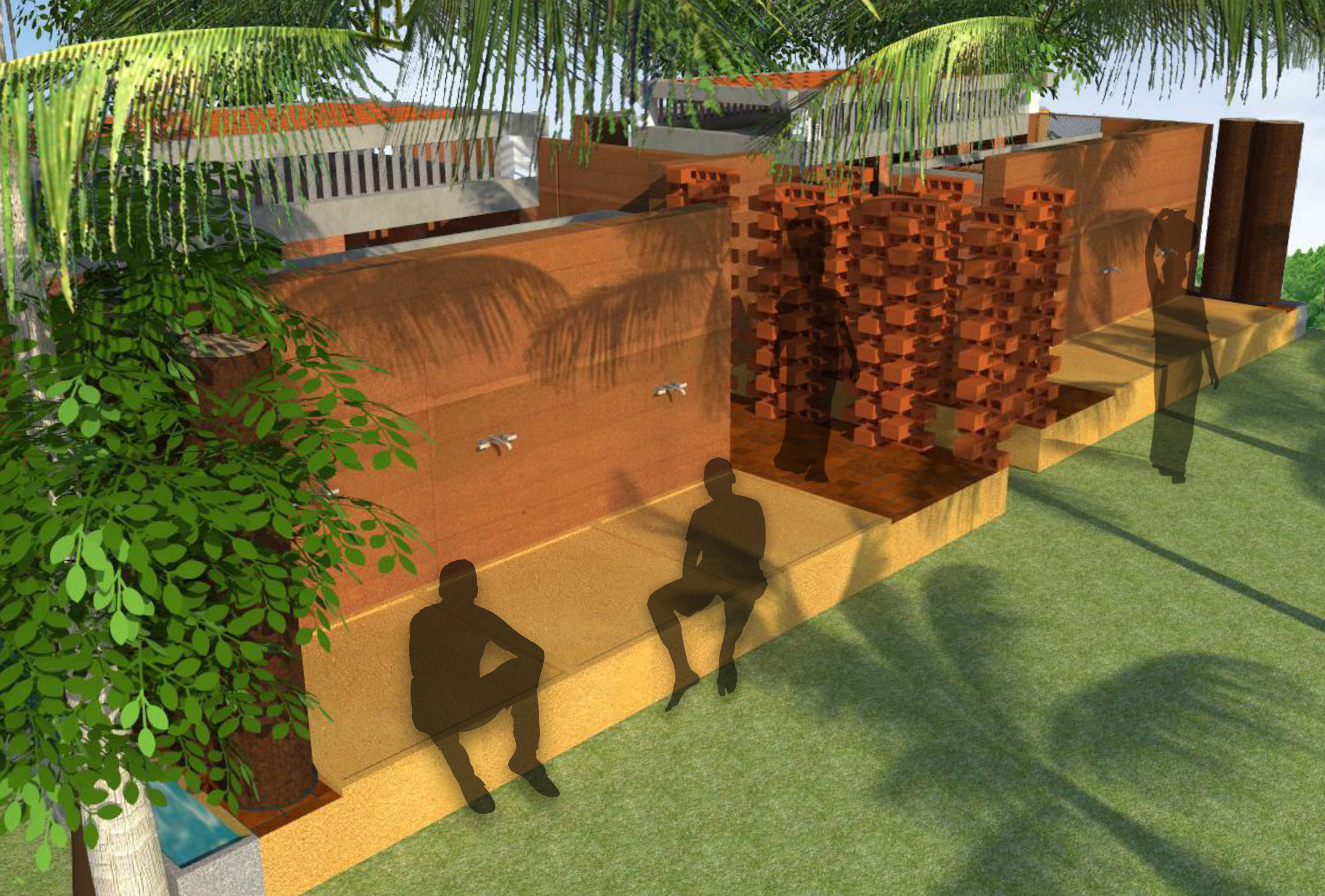
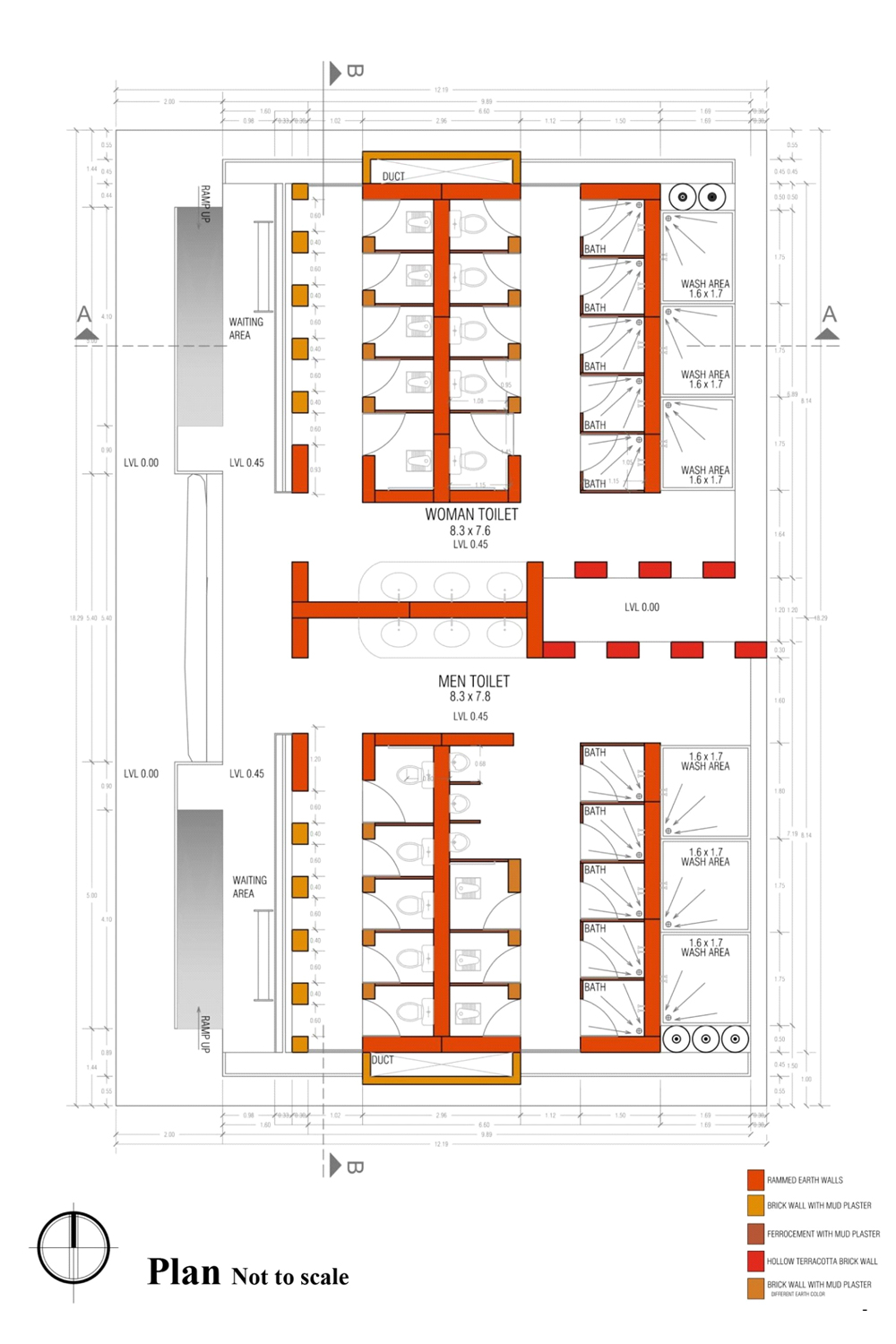
The design strategy was to create a very simple unit that can be built within a short span of time. The materials and the structure and surroundings were to all relate to each other. In the village, the villagers are very used to open toilets where they use the hose pipes or water pipes on the roads to have a bath. Hence, it was taken care that in the design they do not feel that something alien to their daily routine has been forced upon them, just to create sanitation around the village.
The main requirements for a community toilets were as per standards :
Cost is one of the major factors to take under consideration in the toilet complex, it has never occurred to anyone to create a toilet complex out of mud as a building material which would turn out much cheaper and faster for construction. The materials would be locally available and the labor could be the people of the community or village itself as mud construction is very simple and easy for people to learn and supervise.

Building with earth has a great past, also a very bright and promising future. It is definitely an appropriate, cost and energy efficient technology which can promote a sustainable future. Obviously any technique takes time and practice to master, but once the techniques of architecture with mud as a building material is mastered; there are optimum possibilities for a harmonious, durable, agreeable and efficient architecture.
Despite the possibilities and advantages offered by earth materials, building with earth is still not a common practice. Either people do not want to acknowledge the advantage of this material or they do not want to get the burden to organize the site and manage everything by themselves using earth or they think it is only a practice based for the rural class and so on. While this being the thought of the people in the cities the rural population blindly believe in what the urban population preaches. People are not aware of the fact that when mud is available to them, they should make the optimum use of it. The construction of a community using mud is done so as to create an awareness among the rural population as they would then believe that mud is not mere a low class material.
The construction of these mud structures will in turn help the people to realize the various new techniques and they would also be able to build their own structures as mud is a very simple technique and this would further create a work opportunities for a great number of people. While talking about the urban population, even the government has forgotten the importance of a material so rich and traditional as even they promote only concrete structures as they consider it a more convenient building material, not being aware of the fact that rural villages are the major places where they could use mud as a building technique as has now become so advance, locally available and less labor intensive than the usual techniques.
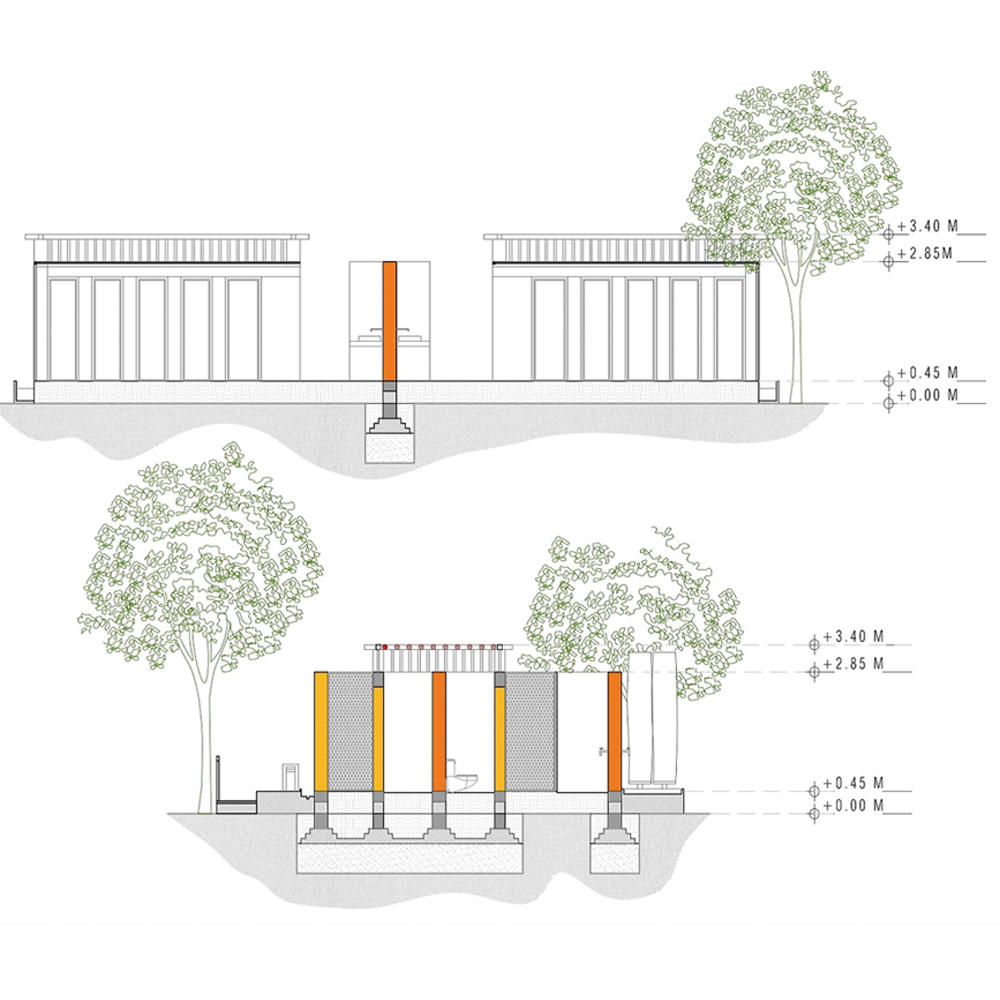
Mud is one of those materials that need to be appreciated and promoted. Mud is one of those few materials that provide multiple uses and advantages. It is a material that behaves as incentive to keep the traditions and cultures alive .It creates an atmosphere so comfortable and affordable for the user, also causes for a cool self-sufficient environment.
How to realize architecture full of light, suppleness, simplicity, imagination and beauty with a heavy and formless mud?
This is the main aim of many architects of the recent times who believe that earth is not just a traditional material but a material that due to its traditions can sustain throughout the modern age and modern construction techniques.
Architects and the government spend a great amount of time making impossible happen, while the things that are possible are never ventured as they are considered too ordinary or simple, but we never realize that simple possibilities lead to multiple possibilities with great satisfaction.
References:
⦁ Laurie Baker Architect’s Official Website – Alternative Building Materials Timeless Mud.html
⦁ Auroville Earth Institute.html
⦁ Clay – Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.html
⦁ Mud – Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.html
⦁ Thesis on earth architecture.html
⦁ Silt – Clay – Mud – Sand What Is The Difference.html
⦁ Soil Groups 8 Major Soil Groups available in India.html
⦁ Soil quality considerations in the selection of sites for aquaculture.html
⦁ Soils in india.html
⦁ Soil quality considerations in the selection of sites for aquaculture.html
⦁ Mud Architecture – Construction Details and Techniques Archinomy.html
⦁ Mastaba – Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.html
⦁ Mud House – RAEL SAN FRATELLO.html
⦁ Mud Architecture – Construction Details And Techniques Archinomy.html
⦁ Muram Flooring The Construction Civil.html
⦁ Floors and its types.html
⦁ Musgum earth architecture in Cameroon Projects.html
⦁ mud for everyone Part 3 Arches.html
⦁ Architectural elements used by ancient Egyptian builders_files.html
⦁ Tamil Nadu state, India Encyclopedia Britannica.html
⦁ Resource Management Soil Groups of TN.html
⦁ Design Resource – Athangudi Tiles – Making Process – 4.html
⦁ Architecture and interior design projects in India – IRRAD, Gurgaon – Ashok B Lall – New Delhi.html
⦁ IRRAD Gurgaon ASHOK B LALL ARCHITECTS.html
⦁ Sharanam – Rural Development Center The Sarvam Trust (Registered charity no 1148419).html
⦁ Total Sanitation Campaign (TSC) Ministry of Rural Development (Govt. of India).html
⦁ Swachh Bharat Abhiyan.html
⦁ Rural Development & Panchayat Raj – Schemes State Schemes2.html
⦁ 10 crore toilets to be constructed by 2019 Government – IBNLive.html
⦁ Articles about Public Toilets – timesofindia-economictimes.html
⦁ Modi has unleashed a mass movement for public cleanliness. But the question of what dirt means in India demands a deeper reckoning Cover Story – India Today.html
⦁ Articles about Public Toilets – timesofindia-economictimes.html
Book References:
⦁ MUD – Laurie Baker
⦁ BUILDING WITH FIRE Baked- Insitu Mud Houses of India: Evolution and Analysis of Ray Meeker‟s Experiments- Aunpama Kundoo_ research paper
⦁ The „State of Play‟ of Sustainable Buildings in India125U n i t e d Na t i o n s En v i r o n m e n t P r o g r a m e
⦁ EARTH BUILDING TECHNOLOGIES AS A KEYSTONE OF THE SUSTAINABLE ARCHITECTURE- AUTHOR: BARBARA CSILLIK
⦁ EARTH AS A RAW MATERIAL- Auroville Earth Institute
⦁ Sustainability of traditional rural mud houses in Tamilnadu, India: Ananalysis related to thermal comfort – A Madhumathi, J.Vishnupriya, S Vignesh
⦁ GUIDELINES ON COMMUNITY & PUBLIC TOILETSGovernment of Odisha Housing and Urban Development Department
⦁ GUIDELINES NIRMAL BHARAT ABHIYAN (July – 2012)
⦁ WATER SUPPLY AND SANITATION – Tamil Nadu Guidelines






